How Are Employee Stock Options Taxed? | The Motley Fool
Difference between the fair market value of the shares as on the date of exercising the option and the amount paid to exercise the option is taxable as per the tax bracket of the employee. The taxable value is called 'perquisite. Difference between the sale value and fair market value as on the exercise date is taxable as capital gains.
If ESOPs are sold after completion of a period of 12 months, the gains on the listed shares will be treated as long term capital gains. If holding period of unlisted shares is lesser than 24 months, the gains will be treated as short term capital gains and will be taxed as per applicable slab rate of the employee.
Click here to read the Mint ePaper Mint is now on Telegram. Join Mint channel in your Telegram and stay updated with the latest business news. Looks like you have exceeded the limit to bookmark the image.
Remove some to bookmark this image. You are now subscribed to our newsletters.
ESOP Shares Issued by a Foreign Company
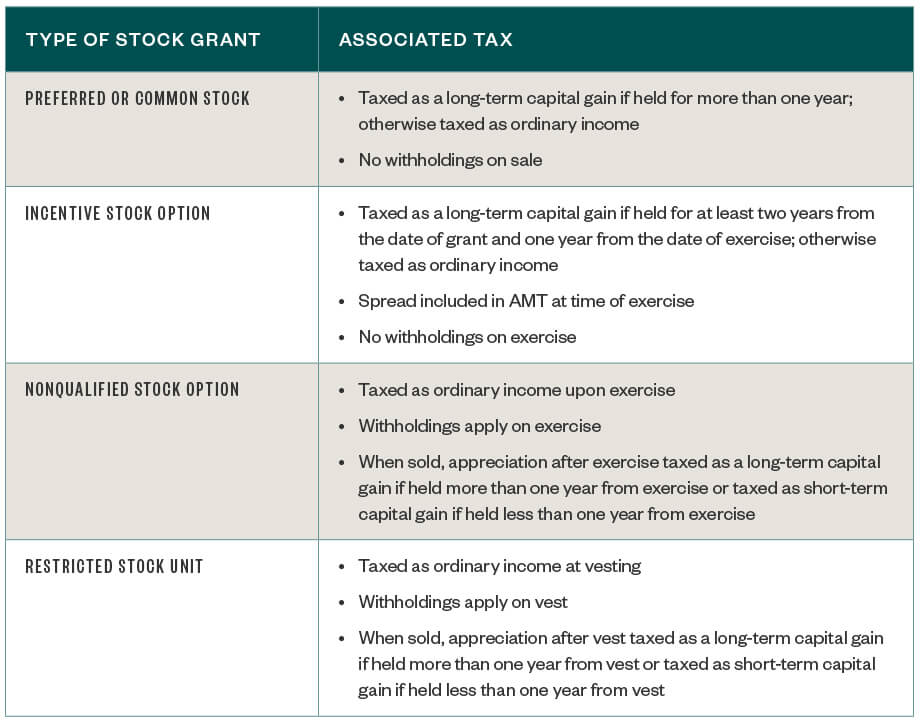
Typically, you face a delay between when you are awarded stock options or restricted stock and when you are fully vested. This is the point when you can exercise your right to purchase the shares. Leave the company before then, and you'll likely forfeit any unvested options. Taxation of stock options depends on what kind you have, and how long you hold those options before selling them. There are incentive stock options which must meet specific rules under the tax code and non-qualified stock options pretty much everything that isn't an ISO.
For non-qualified stock options, generally speaking, you pay taxes when you exercise those options, based on the difference between the so-called exercise price — the amount you were promised you could buy the stock for — and the fair market value at that time. That difference is taxed as ordinary income and subject to payroll taxes, and gives you an adjusted taxable basis of that fair market value.
- What are employee stock options? How are ESOPs taxed?;
- Get the Most Out of Employee Stock Options.
- weizmann forex ltd reviews.
- vanguard forex;
Then when you sell the shares , you'll have either a short- or long-term capital gain or loss based on the difference between that adjusted basis and the sale price. For short-term gains, you pay your ordinary income tax rate. For long-term gains, the tax rate is either zero percent, 15 percent or 20 percent, depending on your annual income. Restricted stock is taxed differently from stock options and it can get even more complicated.
Generally speaking, however, when those shares vest, it is considered compensation and you are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. If you hold on to them for a while, you would incur capital gains taxes for any difference between the vested price and what you sold it for.
Tax is typically withheld by your employer in both cases, although the methods are slightly different.
Get in touch
Before you do much of anything with your company stock, you should put it in the context of your full financial picture. However, it may be hard to estimate tax on capital gains and deposit advance tax in the first few instalments if sale took place later in the year. Therefore when advance tax instalments are being paid, no penal interest is charged where instalment is short due to capital gains. Remaining instalment after sale of shares of advance tax whenever due must include tax on capital gains.
Other considerations involved To properly calculate tax on sale of ESOPs certain other aspects need to be considered as well. Short term or long term gains The rates at which your capital gains shall be taxed depends on the period of holding them. The period of holding is calculated from the exercise date up to the date of sale.
Equity shares listed on a recognised stock exchange where STT is paid on sale are considered as long-term gains when held for more than one year. If sold within one year, they are considered as short-term gains. Long term loss on equity shares is a dead loss and has no treatment, simply because gains are not taxable as well. Listed or unlisted shares The Income Tax Act differentiates between tax treatment of listed and unlisted shares. The tax treatment for shares which are unlisted in India or listed out of India remains the same.
- Taxes on Equity Compensation — The Holloway Guide to Equity Compensation?
- agimat binary option system free download!
- How and When Are Incentive Stock Options Taxable? – Daniel Zajac, CFP®!
- trading signals kse;
That is, if you own shares of an American company, they will not be listed in India. They may be considered unlisted for the purpose of taxes in India.
How to Report Stock Options on Your Tax Return
The shares are short-term when held for less than 3 years and long-term when sold after 3 years. The period of holding begins from the exercise date up to the date of sale. Starting FY , UNLISTED equity shares shall be short term capital assets — when sold within 24 months of holding them long term capital assets — when sold after 24 months of holding them [Applicable for sales made on or after 1st April Residential status Your income is taxable in India according to your residential status.
If you are a resident, all your income from anywhere in the world are taxed in India. On the other hand, if you are a non-resident or resident but not ordinarily resident and have exercised your options or sold your shares, you may have to pay tax outside of India. It makes sure your income is not taxed twice.
Is your company planning to IPO? Here’s what that means for your stock options
Disclosures Several disclosures have been added in income tax return forms for foreign assets. These disclosure requirements are applicable to a resident taxpayer. When options are not exercised On the vesting date the employee gains a right to exercise his option or buy the stocks. But there is no obligation, employee can choose to not exercise his option.